

PCIe
PCI is a well-established interconnect standard which enables connecting components in a complex electrical system.
PCI Express – also referred to as PCIe – as its successor features higher bandwidths, smaller footprints, improved error detection, and many other advantages. Main advantage of PCIe is its easy usage from a software perspective by operating via simple memory-mapped access. A so-called Root Complex acts as the central managing instance, configuring and monitoring the interaction of CPU(s), memory, and PCIe devices.
With the evolution from PCI to PCIe, the standard has adopted to point-to-point serial data transfer, instead of parallel busses.
Products
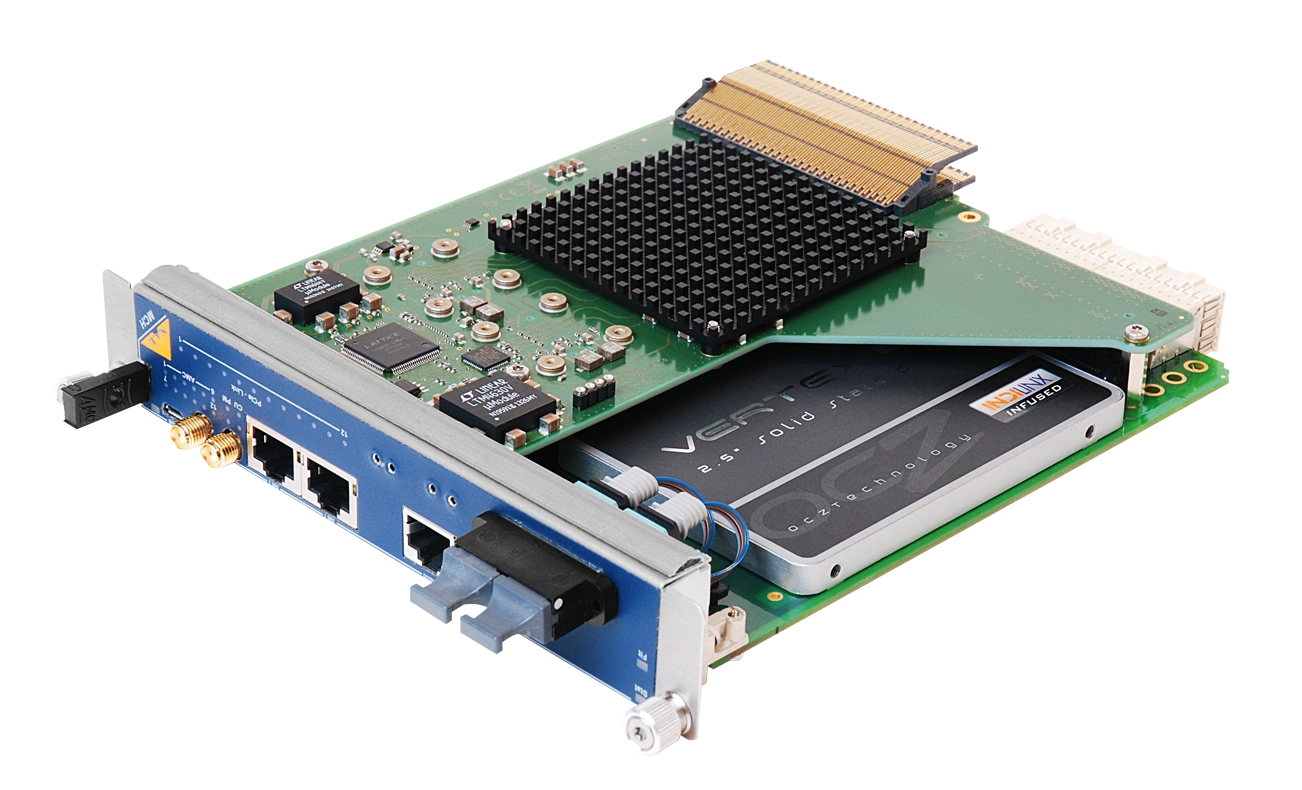
NAT-MCH-PHYS80
- Designated for high demands regarding bandwidth, timing, and precision
- Specialized NAT-MCH-CLK-PHYS mezzanine module
- Power and system management for up to 12 AMCs, 2 CUs, and 4 PMs
- PCIe Gen3 x16 data switching towards backplane and front uplink
- RTM with COMExpress Support
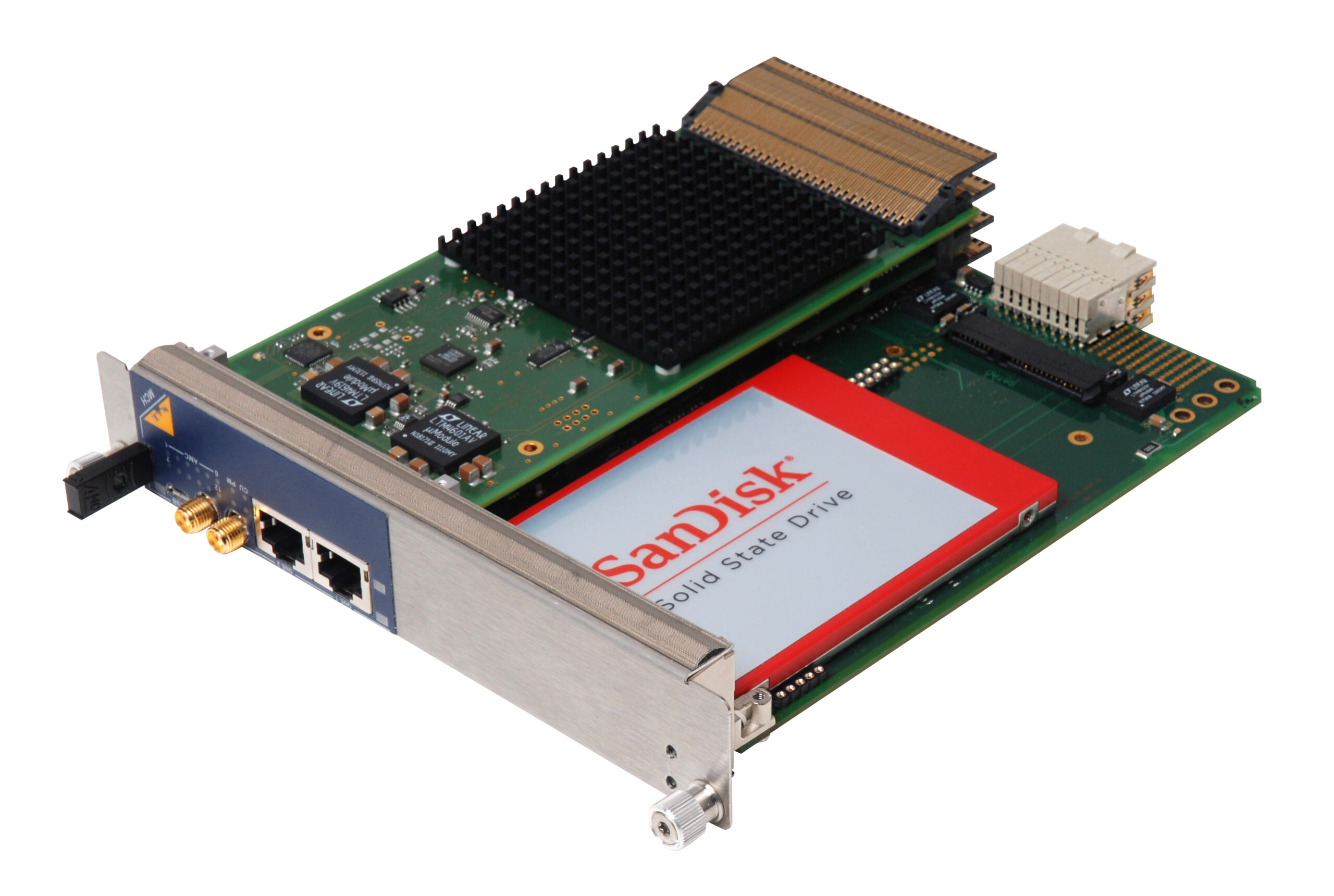

NAT-MCH-PCIex48
- PCIe Gen3 x1 or x4 link to each of the 12 AMCs in an MTCA system
- High bandwidth, non-blocking interconnections for various applications
- Configuration option for Spread Spectrum Clock (SSC) or 100MHz fixed PCIe clock
- PCIe clock can be provided as Fabric Clock (FCLKA) to the AMC slots
- Clustering support for 6 independent clusters with one configurable non-transparent upstream port

NAT-MCH-PCIex80
- PCIe Gen3 x4 link to each of the 12 AMCs in an MTCA system
- Two PCIe Gen3 x8 or one x16 link(s) towards front panel uplink
- PCIe Gen3 x16 link to MCH-RTM
- Higher bandwidths to reduced number of AMC slots (if supported by backplane)
- Clustering support for four virtual PCIe clusters with up to four PCIe Root Complexes
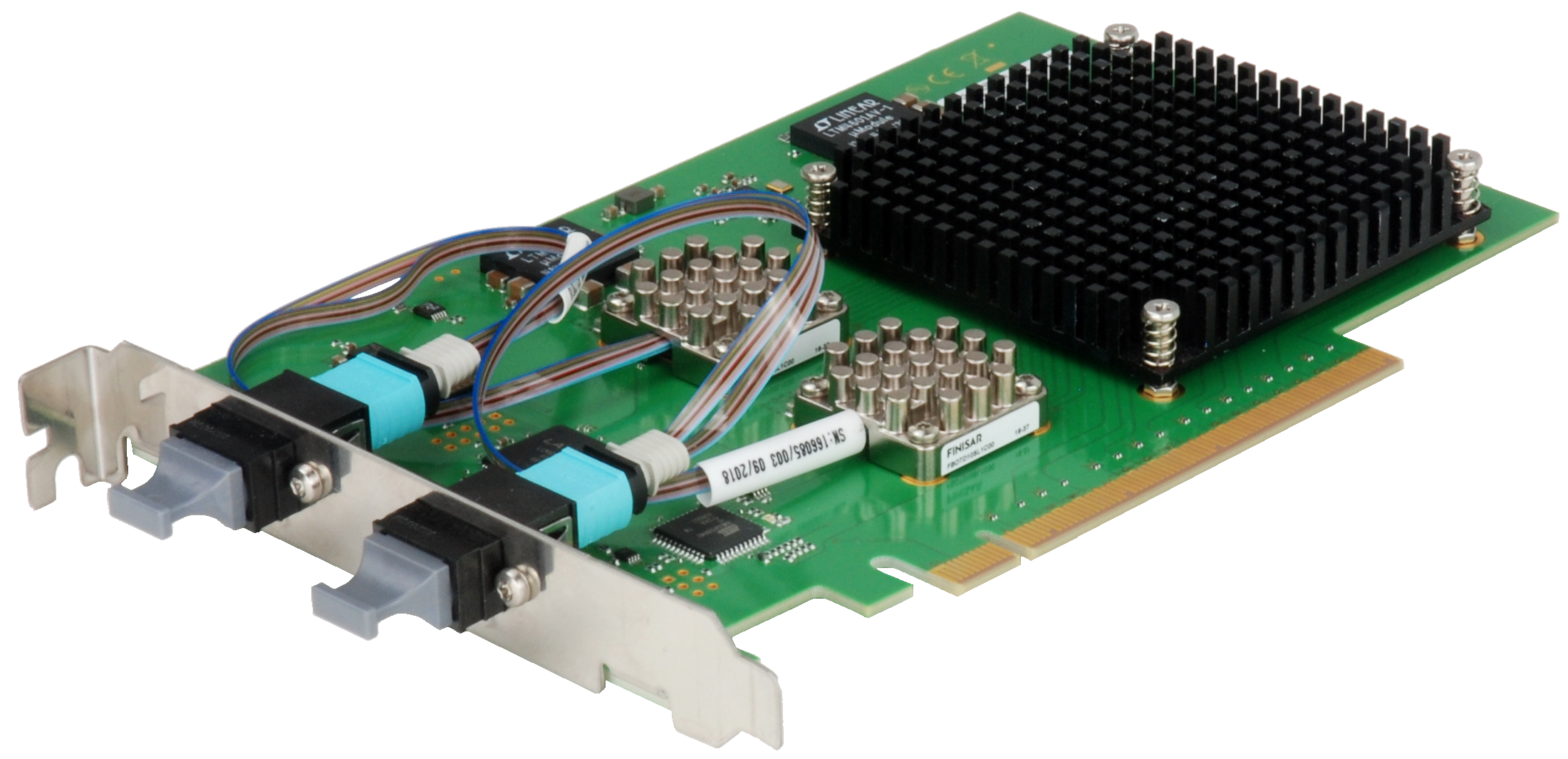
NPCIe-UPLINK-O
- PCIe interface card for operation in PCs / servers
- Optical PCIe Gen3 x8/x16 uplink(s) towards front panel
- Transparent to PCIe host => no special driver required
- SSC isolation support
- PCIe hot-plug functionality
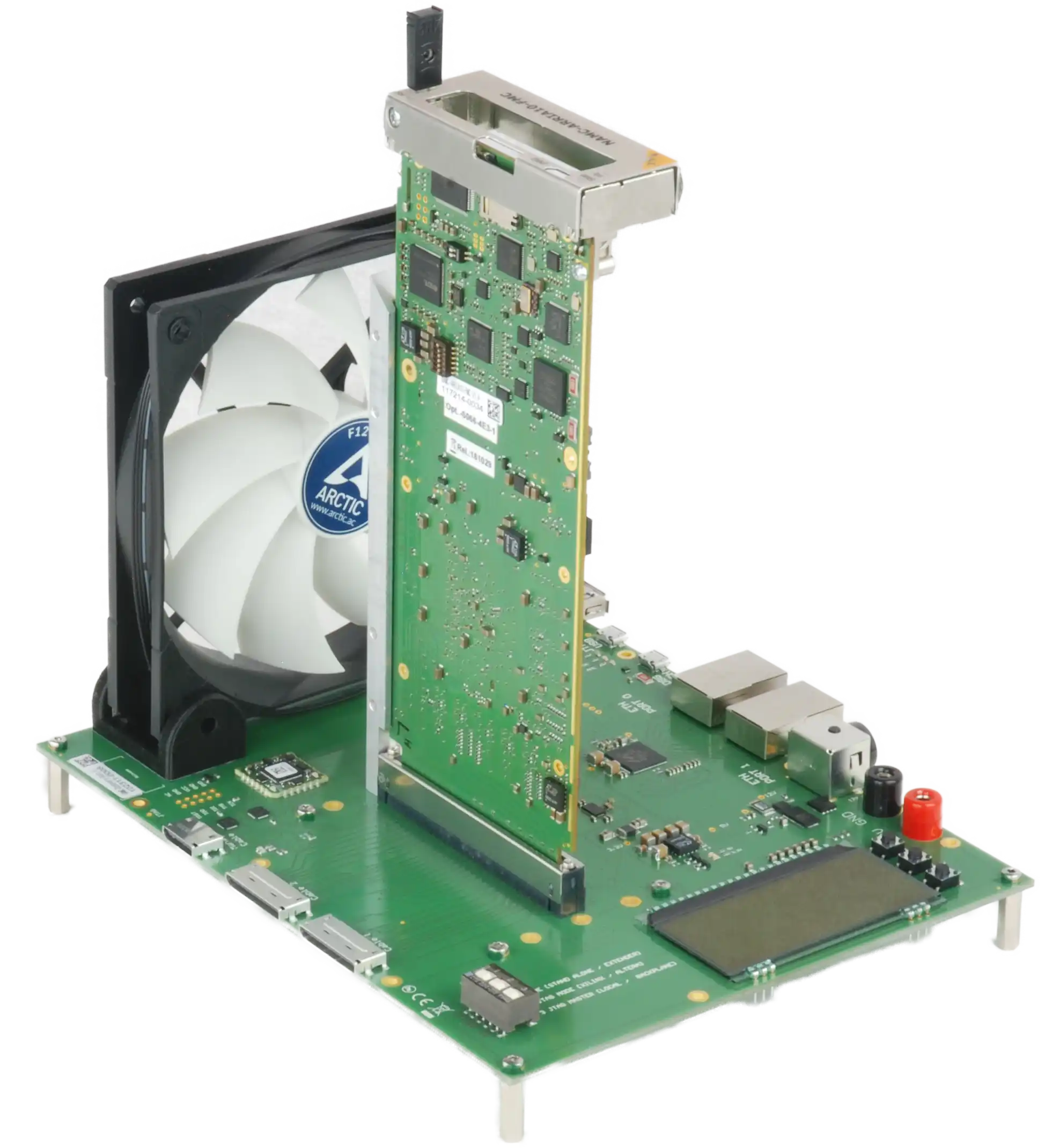

NAT-AMC-DISCOVERY
- NAT-eMCH included on Base PCB
- Support of single- and double-width AMCs in compact, mid-, and full-size form factor
- Operation in standalone mode
- Operation in different extender modes (MTCA / PCIe) – Extension Kits required
- Loopback Mode support
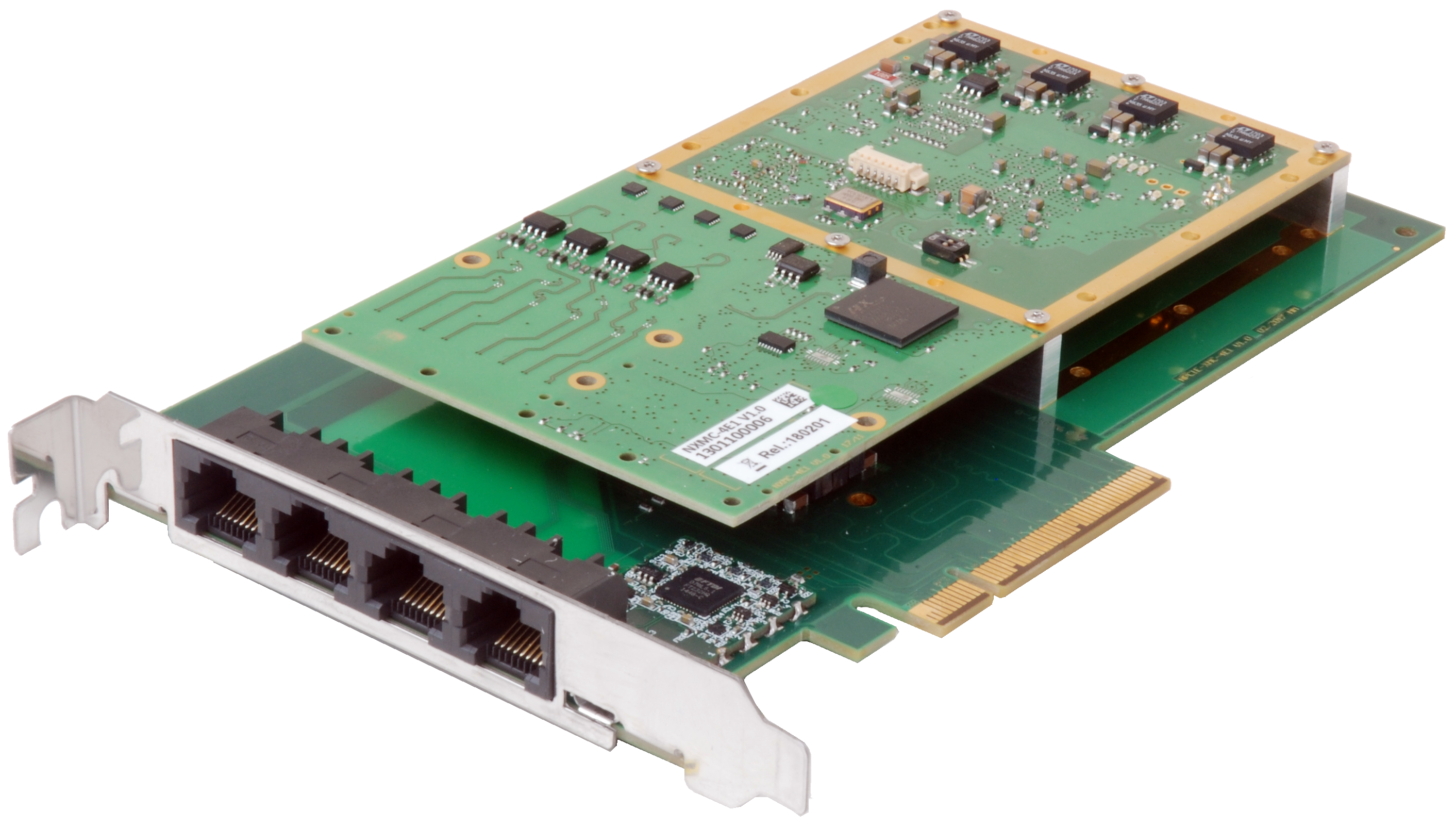
NAT-PCIe-XMC-4E1
- Xilinx Spartan-7 XC7S50 FPGA
- Maxim/Dallas DS26518 E1 / T1 framer
- Broadcom/PLX PEX 8112 PCIe-to-PCI bridge
- 64 MB SPI flash and 512 MB DDR3 DRAM
- Standard height, half-length PCI Express x8 add-in card
NAT-PCIe-8E1T1
- Xilinx Spartan-7 FPGA
- Maxim Dallas DS26518 E1 / T1 framer
- Diodes Incorporated PI7C9X112SL PCIe-to-PCI bridge
- 8x E1 via RJ45 towards front panel
- Standard height, half-length PCIe x1 add-in card